
 [罗戈导读]此篇文章接上篇"CSCP-Module2上篇"以及"CSCP-Module 1: Supply Chain Design"。
[罗戈导读]此篇文章接上篇"CSCP-Module2上篇"以及"CSCP-Module 1: Supply Chain Design"。

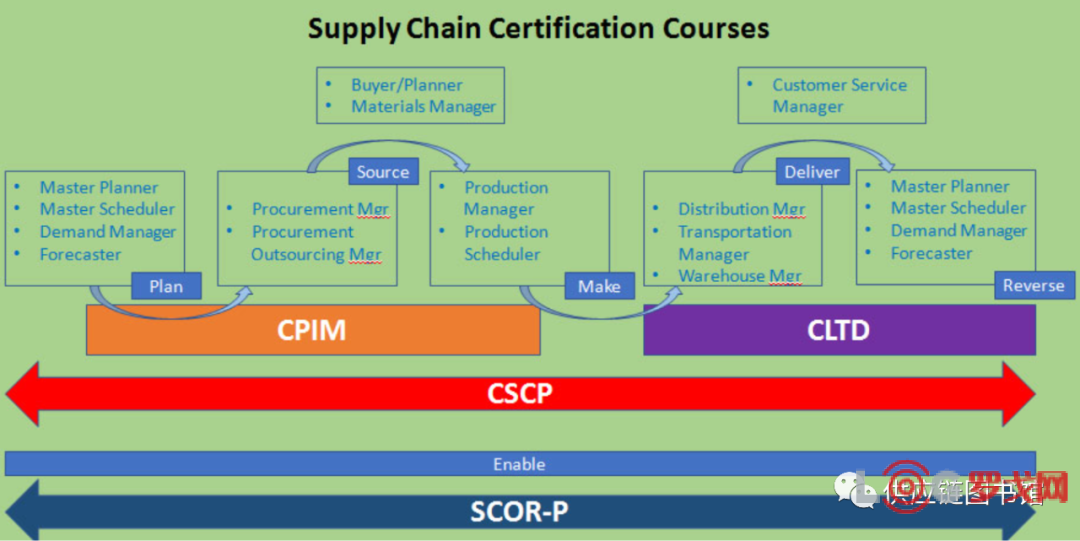
此篇文章接上篇"CSCP-Module2上篇"以及"CSCP-Module 1: Supply Chain Design",如果想看第一模块及第二模块上篇,此文下附链接可跳转。
因教材本身目前是英文版,笔记同为英文版,偶尔穿插中文注释,及相对原教材的摘取删减。
Chapter 10: Logistics
Topic1: Introduction to logistics
Logistics Value proposition
Service
Cost minimization
概念:risk pooling
A method associated with the management of inventory risk
A method of reducing stock outs by consolidating stock in centralized warehouses
Topic2: 3PL, 4PL
(4PL is taking over the entire logistics operation and subcontracts some specific functions)
Outsourcing consideration
Correct costs?/ potential savings in time + improved quality of service to customer
What customer skills does the contractor possess?
Contractor's special strengths?
Especially when consider 4PL, will contractor hire most-qualified partners?
Topic3: Expediting
Topic4: Delivery conditions/shipping patterns
Order fulfillment channels 渠道/途径/路线
Distribution channel strategy is determined during strategy formation;
Some tactical selections can be determined during network design;
(有5种channel,each with 如下特征,5种channel列举如下:)
1.different levels of service outputs: break-bulking, special convenience, waiting and delivery time, variety and assortment
2.different channel design intensity (market penetration, distribution-integrative, distribution
Manufacturer storage with direct delivery
Manufacturer storage with drop ship
Use transload and cross-dock facilities
High-value, sporadic demand items
Make to order, customized/postponed items that can be finished when order arrive
Shipment in small lots, transportation cost increase, lead time increase
Manufacturer doesn't need to maintain a sales force
Manufacturer to distribution center to retailer
Inventory intensive
Mass-produced, inexpensive goals with high competition
Strong product availability, customer service level high
Independent distributor with omni-channel network
Independent aggregator with e-business network
Depend more heavily on direct marketing to individuals through its own heavily branded website eg. Alibaba, amazon;
Chapter 11: Warehouse management
Topic1: Warehouses objectives & planning
Warehouse ownership
Private warehouses
Public warehouses (available in a variety of configurations)
Contract warehousing (tailored service)
Determine the right number of warehouses: inventory/transportation/customer service/overhead cost
Determine the right locations for warehouses
Warehouse capacity forecasting & planning
Topic2: Warehouse capabilities
Warehouse function
Consolidation of materials for shipping
Break-bulk and cross-dock facilities (consolidated, full-trailer shipment into facility, or out of facility)
Postponement
Stockpiling seasonal inventory (anticipation)
Spot-stocking advance shipment
Assortment (ensure short customer lead time)
Mixing (similar to break-bulk)
Chapter 12: Transportation
Topic1:Objective, constraints
Product movement
Temporary storage
Line haul costs
Vehicle costs
Driver/operator costs
Vehicle operating costs
General & administrative costs
Insurance & security costs
Topic2:Transportation modes
Railway transport
Motor carriers
Truck load TL: Travel straight from loading dock to destination
Less than truck load (LTL): truck often stop at intermediate
Specialty: eg. UPS
Water transport
Pipeline transport: highest fix cost, lowest variable cost
Air transport
Intermodal transport
Topic3:Mode and carrier selection
Carrier
Common(public)
Private
Contract
Exempt(豁免承运人)
Chapter 13: Monetary, regulatory, trade considerations
概念:
trade credit/ open account: unsecured, trust-based transaction between parties
Bill of lading(B/L): Shipping company issue a B/L with buyer as a way of demonstrating ownership of goals
Letter of credit(L/C): Standard method of financing international trade
Currency issues
Currency exchange risk
Currency hedging: technique used to offset risks associated with changing value of currency/currency futures
Cash to cash cycle time/cash conversion cycle: a key metric for measuring
The efficiency of the flow of funds
Incoterm
Customs
Custom house brokers: assist importers by moving shipments through customs, ensure all docs required to pass customs is complete
Ship brokers and ship agents: assist exporters with details of arranging transport. Eg. Ship headed for port, arrange for arrival, berthing, clearance
Freight forwarder
Import
Export docs
Bill of lading & air waybills/airway bill of lading
Export B/L; ocean B/L; orders B/L; clean B/L
Free trade zone好处,区域贸易组织,贸易集团
Trading docs: an agreement between countries intended to reduce/remove barriers to trade within member countries.
Chapter1: Segmentation
Topic1: Segmentation & customer-focused marketing
Market segmentation 应用的primary reason: increase organization's profit over long term
Customer segmentation: divide a customer in specific ways relevant to marketing
Customer-focused marketing: require identify & understand market segmentation
Customer-driven
The reason to define market segment is no single set of customer
Logistics and marketing strategy must focus on customer segments
Benefits of segmentation
Niche /customization, marketplace is segmented everyday
Benefits organization, better return on promotional budgets
Topic2: Customer segmentation
Define segments: May occur in a customer-focused strategy by 3 types
Segmentation by customer value,
the greater the customer value, the better the treatment customer recieves
Segmentation by customer needs,
Specific product/ service features, contact channels/ logistic channels
Value profile: to understand what customer want, why, how much
Value proposition:
draft details how each segment's perception of value will be fulfilled by product/service
A key part of promotional strategy & customer relationship
Segmentation by preferred channels
Customer may use websites to obtain etc.
Some business sectors
Reward customers that use tech channels
Educate customers on the benefits of a particular channel
Segmenting customers
Acquire customer information 的方法
Market research
Sources of customer infor.
Market intelligence
Transaction record
Sales representative
Service representative
Distribution points
Purchased data
Voice of customer (VOC) insightful things, related to RFID
Developing solutions to existing service/product problem
Continual improvement
May help business understand customer expectations/needs
Topic3: Segmentation of suppliers/ other SC partners
Supplier segmentation
好处:increase responsiveness without significantly increase costs; ideal for organizations pursuing strategies other than low cost
类型forms:
Ideal relationship type
Supplier capabilities--->based on supplier's ability to deliver on key business objectives at the core of their strategy
Customization vs standardization
Level of innovation
Lead times
Chapter 2: CRM(Customer Relationship Management)
定义:include account management, catalog and order entry, payment processing credits and adjustments
Long-term focus
Topic1: Scope of CRM
Sales operation: most functional activity in CRM & rely heavily on technology
Analysis
Customer info. Dissemination (timely, focused infor to right group)
Relationship building & collaboration
Lifetime customers lower total marketing cost
Easier to satisfy lifetime customer
Lifetime customers offer increased revenue & profit opportunities
Topic2: CRM strategy
Components of CRM strategy
EBS (Enterprise Business System)--->link with ERP
Web system
Marketing (heart of customer management)
External data
CRM application: 3个组成部分:operations, collaborative, analytical CRM
Analytics
Service
CRM processes
Focus on improving time-to-market
A formal monitoring & feedback process
Review the metrics that assess performances
Process improvement using PDCA
CRM organizational structures
CRM technology
Product's or service's stage in life cycle
Development stage
Introducing stage: support promotional program (advertising increase)
Growth stage: customer care must be sustained
Maturity stage: focus on entire its competitor's customers to switch; attract new customers
Deliver stage
Customer type or segment
Customer strategy for customer segments
Strategy for segmentation by demographics, attitudes, psychological profiles
Customer value strategy
Service-minded customer strategy: technology, call center is the heart of business
Retail customer strategies: price, quality, the bundle of service surrounding the products
B2B customer strategies
Complementary core competencies
Knowledge of customer's business requirements
Continuous improvement
Strategies for reaching customers via technology channels
Strategies for customer relationship types (4种)
A key purpose of a CRM strategy is to allow an organization to address various types of prospects & customers it services at different strategies in their particular life cycle
Prospective customers
Vulnerable customers (churn)
Win-back customers rapid communication
Loyal customers
Cross-selling (similar listing)
Up-selling (more expensive listing)
Chapter 3: CRM performance & measurement
Topic1: Performance management (measure customerservice & customer satisfaction)
Customer service
Response to inquires
Should be prompt and accurate
Measure include tracking the volume, response time, trends of such complaints
Order processing
Should be fast and accurate
Metrics: order cycle time, etc.
Level of service
6个right
Metrics: the percentage of orders shipped complete & on-time, the number of backordered items, the average age of backorders, value of backordered items
Product or service quality
Measured by cost of quality issues
Eg. Number of executive complaints, defect rates etc.
Customer satisfaction
Customer complaints as a measure
VOC more meaningful
Quality of channels service: evaluate trust of channel; customer feel respect; effectiveness of problem resolution
Some approaches to measure customer satisfaction level
Voice of customer
Transaction customer feedback questionnaires
Monthly/quarterly customer feedback questionnaires
Participation in performance reviews
Collecting & responding negative comments on internet
Topic2: CRM technologies
Charter 4: SRM
Topic1: Introduction
定义:oftenautomating procure-to-pay business process, evaluating supplier performancesexchange infor with suppliers
Strategic sourcing
Focus on long-term relationships with trading partners
IT-->Automation of RFQ etc.
Focus on total cost of ownership, collaborative
Topic2: Supplier selection
Selection criteria
Strategic supply plan
Technical specification
Desired quality
Supplier financial strength
Costs: TCO: COGS(material, labor, overhead)
Alignment with SC needs
Corporate social responsibility polices
Supplier certification
ISO(third-party supplier certification)
Chapter 5: SRM strategy
Topic1: Strategies alliance
好处:add value to products; able strategic growth etc.
Topic2: Supplier performance management
Supplier performance measurement
Supplier rating systems
Setting supplier performance measures & standards
Methods of sharing ratings with suppliers
Scorecards
Performance alerts
Surveys
Chapter 6: SRM technology
Components of SRM system
Chapter 7: Linkages between CRM & SRM
Section C: Manage reverse logistics
Chapter 1: Reverse logistics
Topic2: Strategy & design for reverse logistics
Reverse infor. Cash product flow
Warranty strategy & design
Return authorization strategy and design
Reduce the number of returns without having too many unintended consequences for customer service, sales
For B2B, a lot-size return policy
Logistical network design & strategy
TCO analysis: ->consider whether all or part of function will be contracted out to 3PL;
Life cycle design
Topic3: Reverse logistics benefits & costs
Can generate revenue
Chapter 2: Waste consideration
Reduce use of resources 4/3/3rule
Reuse
Recycle
Recover energy
Disposal in landfill
Waste exchange & hazardous waste
后续模块将持续更新,敬请关注与期待。

年营收643亿,净利88亿,航空货运三巨头业绩出炉
1453 阅读
人工智能深度学习简史(1956~2024)
1458 阅读
老牌跨境物流企业爆雷,资金链断裂
1230 阅读买还是租,物流企业持有新能源车的最佳姿势
1093 阅读汽车供应链变革风暴来袭?!一汽、东风、吉利、比亚迪、小米等集体官宣账期缩至60天
1023 阅读从高州到西安,顺丰跨越1800公里的甜蜜接“荔”!
998 阅读极兔速递参与中国(广东)—东盟贸易促进交流会,分享“最后一公里”解决方案
995 阅读顺新晖和宁德时代签署战略合作协议,共建“零碳冷链”生态圈
952 阅读淘宝首次火箭送快递实验成功
937 阅读2025 LOG低碳供应链物流 杰出贡献奖
862 阅读